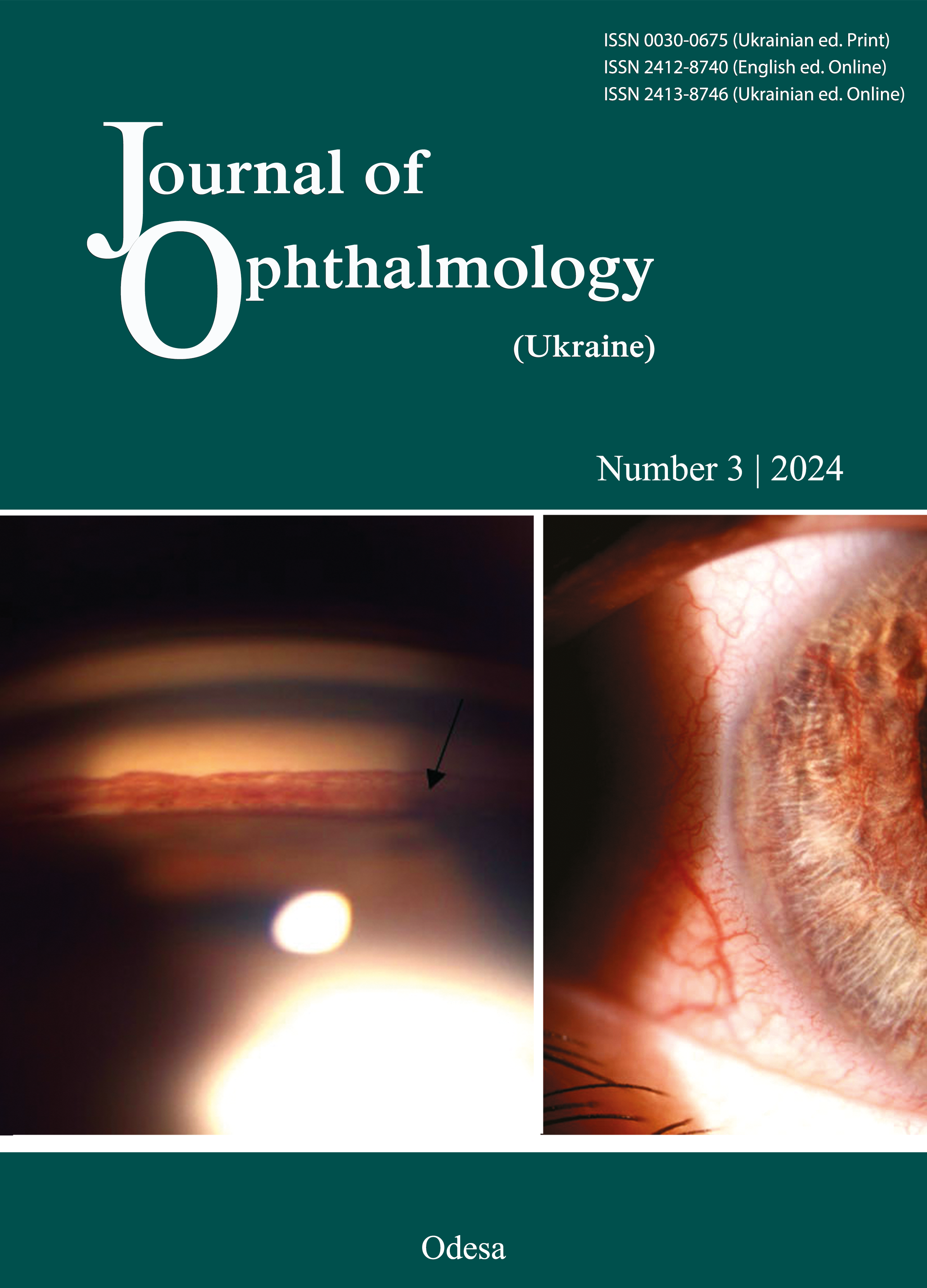
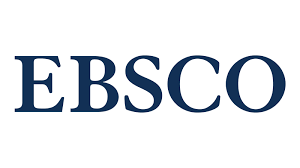In vitro and in vivo study of the biocompatibility and adjacent soft tissue response to synthetic polyvinyl formal hydrogel implant
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31288/oftalmolzh202434551Keywords:
hydrogels, orbit, orbital and periorbital area, biocompatibility, implantationAbstract
Background: Given a rising tendency in the rate of ocular trauma, there is an increasing need in surgeries for orbital, ocular adnexal and periorbital reconstruction. The susceptibility to resorption is a common drawback of the biological tissues used as a plastic material in contemporary orbital surgery. Non-biological hollow porous polyvinyl formal (PVF) hydrogel implants capable of integration with adjacent biological tissues offer a new opportunity for reconstructive surgery.
Purpose: To examine the in vivo and in vitro biocompatibility of a synthetic PVF-based hydrogel implant material.
Material and Methods: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis; in vitro evaluation of the biocompatibility of the PVF hydrogel implant material in terms of its cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and effects on marker enzymatic activities of L929 fibroblasts; and in vitro study on implant incorporation.
Results: A cross-linked polyvinyl formal hydrogel for orbital endoprosthesis surgery was synthesized. Our in vitro cytotoxicity and genotoxicity tests of the hydrogel and tests of its effects on marker enzymatic activities of L929 fibroblasts demonstrated safety. All hydrogel implant samples, after being sealed into polypropylene bags and autoclaved for 15 min at 121 °C and 1.04 atm steam pressure, were found to be sterile. In all rats in which the hybrid hydrogel implant was placed subcutaneously in the back, there was prompt relief of edema at the site of postoperative suture. The inflammatory reactions seen in the tissues adjacent to the implant included mostly mild diffuse lymphocytic infiltration close to the implant surface, with no inflammatory reactions seen at the sites more remote from the implant.
Conclusion: Our in vivo and in vitro study of the PVF hydrogel demonstrated its high biocompatibility in terms of its cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and effects on marker enzymatic activities of fibroblast cells, with no post-implantation complications, but a step-by-step improvement in the relationship between the implant and adjacent tissues. The findings of this study allow us to recommend the developed PVF hydrogel for further research on the potential for using it as an implant for filling postoperative cavities and endoprosthesis in orbital and periorbital reconstruction.
References
Tselomudriy AI, Venger GE, Rizvaniuk AV, Pohoreliy DN, Putienko VA. [Peculiarities of surgical rehabilitation of soldiers with battle eye wounds in modern conditions]. In: [Abstracts of the scientific and practical conference with international participation «Filatov Memorial Lectures 2016», dedicated to the 80th anniversary of the Filatov Institute of Eye Diseases and Tissue Therapy of NAMS of Ukraine and 14th Black Sea Ophthalmological Congress]. 19-20 May 2016; Odessa, Ukraine; p. 95. Ukrainian.
Uvarova IV, Maksymenko VB. [Bio‐compatible Materials for Medical Products. Educational Manual. Biomedical Engineering Department. National Technical University of Ukraine "KPI")]. Kyiv: KIM, 2013. Ukrainian.
Phillips TJ. Cultured epidermal allograft - a permanent or temporary solution? Transplantation. 1991 May;51(5):937-41. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-199105000-00001
Samchenko YuM, Dybkova SM, Maletskyy AP, Kernosenko LO, Gruzina TG, Pasmurtseva NO, et al. Antimicrobial effects of hydrogel implants incorporating gold nanoparticles and albucide and developed for reconstructive surgery in the orbit and periorbital area. Journal of Ophthalmology (Ukraine). 2023; 5(514):27-33. https://doi.org/10.31288/oftalmolzh202352733
Samchenko YuM, Maletskiy AP, Bigun NM, Dolynskyy GA, Kernosenko LO, Pasmurtseva NO, et al. Dynamics of depositing and diffusion of drugs (chlorhexidine, 5-fluorouracil and doxorubicin) in hydrogel implants with different hydrogel crosslinking densities. Journal of Ophthalmology (Ukraine). 2020;3:53-60. https://doi.org/10.31288/oftalmolzh202035360
Maletskyy A, Samchenko Yu, Bigun N. Improving the Antitumor Effect of Doxorubicin in the Treatment of Eyeball and Orbital Tumors. In: Hilal Arnouk, Bassam Hassan, editors. Advances in Precision Medicine Oncology. London: IntechOpen; 2021. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.95080
Biological evaluation of medical devices. Part 12: Sample preparation and reference materials. Fourth edition 2012-07-01. Reference number ISO 10993-12:2012(E) - 28 р. 2. International Standard ISO 10993-1, «Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 1: Evaluation and testing within a risk management process» - June 16, 2016.
Methods in Molecular Biology. In Situ Detection of DNA Damage. Methods and protocols. Ed. by Vladimir V. Didenko. 2002; 203:299.
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265-275. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
Prokhorova MI, editor. [Methods of biochemical research: Lipid and energy metabolism]. Leningrad: LGU Publishing House; 1982. Russian.
Varbanets LD, Zdorovenko GM, Knirel YuM. [Methods of endotoxin research]. Kyiv: Naukova Dumka; 2006. Russian.
[On the approval of the "Technical regulation on active implantable medical products": Order № 755 of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine of 2 October, 2013, as amended on 30 November, 2022]. Ukrainian. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/755-2013-%D0%BF#Text
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Samchenko Yu. M., Dybkova S. M., Maletskiy A. P., Kernosenko L. O., Artiomov O. V., Gruzina T. G., Reznichenko L. S., Poltoratska T. P., Pasmurtseva N. O., Zholobak N. M., Podolska V. I., Mamyshev I. Ie., Volobaiev I. I., Bigun N. M.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) that allows users to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author as long as they cite the source.
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors hold copyright immediately after publication of their works and retain publishing rights without any restrictions.
- The copyright commencement date complies the publication date of the issue, where the article is included in.
DEPOSIT POLICY
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) during the editorial process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Post-print (post-refereeing manuscript version) and publisher's PDF-version self-archiving is allowed.
- Archiving the pre-print (pre-refereeing manuscript version) not allowed.