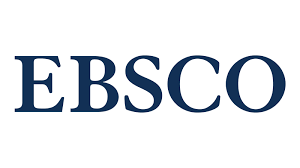Surgical strategy for the treatment of craniofacial tumors with intracranial, extracranial and intraorbital extensions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31288/oftalmolzh202314651Keywords:
craniofacial tumors, transbasal approach, subcranial approachAbstract
Background: Surgical treatment of craniofacial tumors with intracranial, extracranial and intraorbital extensions requires several surgical teams of different specialties (neurosurgery; ear, nose and throat surgery; and eye surgery (for a separate surgical approach)) to be involved. In addition, because craniofacial approaches require creating several surgical fields, the duration of surgery per se is rather long. The conventional transbasal Derome approach is less traumatic than the anterior craniofacial resection and requires no additional dissections of the face. The subcranial approach (a modification of the transbasal Derome approach) may be a low-invasive alternative to the transbasal Derome approach.
Purpose: To assess the efficacy of surgical treatment for craniofacial tumors with intracranial, extracranial, and intraorbital extensions.
Material and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 88 patients with craniofacial tumors (particularly, 66 malignant tumors and 25 benign tumors). Of the 88 patients, 12 (14%) were treated with the transbasal Derome approach, and 76 (86%), with the subcranial approach (via the frontal sinus).
Results: The percentage attributed to total tumor excision (with clear wound margins) was the same (92%; 11/12 and 70/76 patients, respectively) for the groups of patients treated with subcranial and transbasal approaches. Patients with subtotal tumor excision (7/88 or 8%) had malignant tumors, and the rate of subtotal tumor excision was 8% (1/12 and 6/76, respectively) for the groups treated with the former and latter approaches. Mean duration of surgery was significantly shorter in the subcranial approach than in the transbasal Derome approach (291 ± 24 minutes versus 372 ± 48 minutes; р < 0.0000).
Conclusion: Craniofacial tumors with intracranial, extracranial and intraorbital extensions can be totally simultaneously excised by transbasal approaches. A modification of the transbasal Derome approach, the subcranial approach (via the frontal sinus) to craniofacial tumors, can be performed easier and faster, is less traumatic, can be lateralized, and showed the same rate of total tumor excision compared to the transbasal Derome approach.
References
Aftahy AK, Barz M, Wagner A, et al. The transbasal approach to the anterior skull base: surgical outcome of a single-centre case series. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):22444. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80255-8
Ciechomski J, Aufgang R, Villanueva L, Demarchi V. Subcranial approach in pediatric craniofacial surgery. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2010;3(4):231-236. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1268521
Derome PJ. The transbasal approach to tumors invading the base of the skull. In: Schmidek HH, Sweet WH, eds. Operative Neurosurgical Techniques: Indications, Methods, and Results. Boston: Grune & Stratton; 1982:357-379.
Feiz-Erfan I, Spetzler RF, Horn EM, et al. Proposed classification for the transbasal approach and its modifications. Skull Base. 2008;18(1):29-47. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-994292
Fliss DM, Abergel A, Cavel O, Margalit N, Gil Z. Combined subcranial approaches for excision of complex anterior skull base tumors. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133(9): 888-896. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.133.9.888
Fliss DM, Gil Z. The Subcranial Approach to the Anterior Skull Base. Atlas of Surgical Approaches to Paranasal Sinuses and the Skull Base. 2016: 139-152. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-48632-0_5
Fliss DM, Zucker G, Amir A, Gatot A. The combined subcranial and midfacial degloving technique for tumor resection: report of three cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(1): 106-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-2391(00)80027-0
Gil Z, Margalit N, Fliss DM. Open Surgical Approaches to the Anterior Skull Base and Paranasal Sinuses. In: Gil Z., Fliss D. (eds) Tumors of the Skull Base and Paranasal Sinuses. Head and Neck Cancer Clinics. Springer, 2012. New Delhi. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2583-6
Gil Z, Spektor S, Abergel A, Cohen JT, Khafif A, Shlomi B, et al. [The subcranial approach for tumors involving the anterior skull base]. Harefuah. 2003 Jun; 142(6): 416-20, 487, 486.
Jittapiromsak P, Wu A, Deshmukh P, et al. Comparative analysis of extensions of transbasal approaches: effect on access to midline and paramedian structures. Skull Base. 2009;19(6):387-399. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1224773
Joseph ST, Thankappan K, Buggaveeti R, Iyer S. Pneumosinus Dilatans Helping Subcranial Resection in a Patient with Advanced Ethmoid Malignancy. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2015;8(3):218-220. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1393736
Kim YS, Moon KS, Kim GW, et al. Role of Craniofacial Resection for Malignant Tumors Involving the Anterior Skull Base: Surgical Experience in a Single Institution. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2015;3(2):81-88. https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2015.3.2.81
Laedrach K, Remonda L, Lukes A, Schroth G, Raveh J. Evaluation of the Contribution of CAS in Combination with the Subcranial/Subfrontal Approach in Anterior Skull Base Surgery. Skull Base. 2001;11(1): 59-76. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-12785
Liu JK, Decker D, Schaefer SD, Moscatello AL, Orlandi RR, Weiss MH, et al. Zones of Approach for Craniofacial Resection: Minimizing Facial Incisions for Resection of Anterior Cranial Base and Paranasal Sinus Tumors. Neurosurgery. 2003; 53(5): 1126-1137. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000088802.58956.5A
Plinkert PK, Zenner HP. Transfazialer Zugang, kraniofaziale Resektion und Midfacial Degloving bei der Chirurgie bösartiger Tumoren der vorderen Schädelbasis und der angrenzenden Nasennebenhöhlen [Transfacial approach, craniofacial resection and midfacial degloving in surgery of malignant tumors of the anterior cranial base and adjacent paranasal sinuses]. HNO. 1996;44(4): 192-200.
Raso JL, Gusmão S. Transbasal approach to skull base tumors: evaluation and proposal of classification. Surg Neurol. 2006;65 Suppl 1:S1:33-1:38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.11.037
Ross DA, Marentette LJ, Moore CE, Switz KL. Craniofacial resection: decreased complication rate with a modified subcranial approach. Skull Base Surg. 1999;9(2): 95-100. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1058155
Wigand ME, Iro H, Bozzato A. Transcranial combined neurorhinosurgical approach to the paranasal sinuses for anterior skull base malignancies. Skull Base. 2009;19(2): 151-158. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1096200
Sakata K, Maeda A, Rikimaru H, Ono T, Koga N, Takeshige N, et al. Advantage of Extended Craniofacial Resection for Advanced Malignant Tumors of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses: Long-Term Outcome and Surgical Management. World Neurosurgery. 2016; 89: 240-254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.02.019
Gil Z, Patel SG, Bilsky M. et al. Complications after craniofacial resection for malignant tumors: are complication trends changing. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2009; 140 (2): 218-223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2008.10.042
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Palamar O.I., Huk A.P., Lukach E.V., Okonskyi D.I., Teslenko D.S., Davydenko B.O.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) that allows users to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author as long as they cite the source.
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors hold copyright immediately after publication of their works and retain publishing rights without any restrictions.
- The copyright commencement date complies the publication date of the issue, where the article is included in.
DEPOSIT POLICY
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) during the editorial process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Post-print (post-refereeing manuscript version) and publisher's PDF-version self-archiving is allowed.
- Archiving the pre-print (pre-refereeing manuscript version) not allowed.